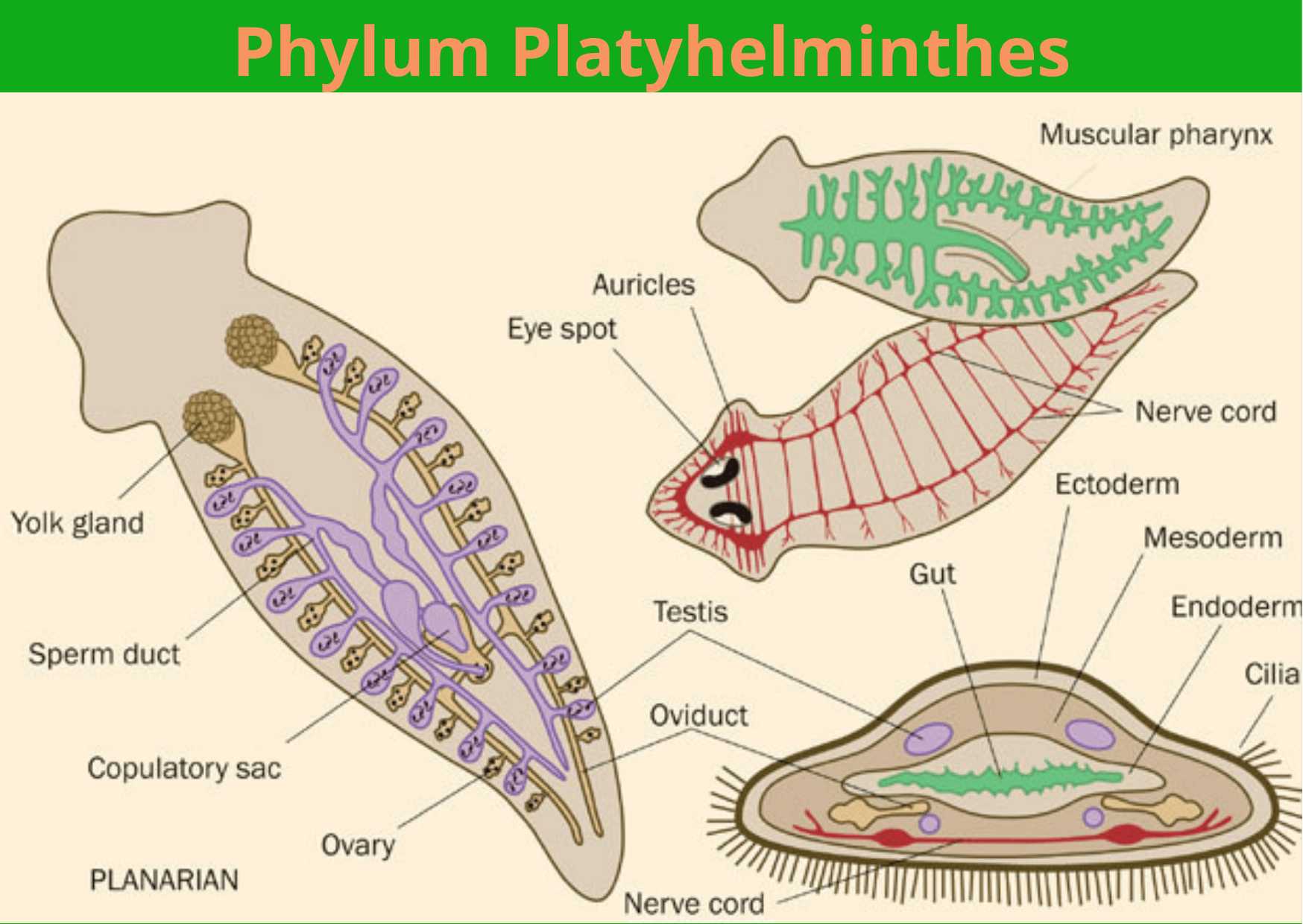
Phylum Platyhelminthes are commonly called as flatworms. The term Platyhelminthes is derived from Greek word platys=flat and helminths=worms. It was coined by Gegenbaur. According to research, there are around 25,000 species of flatworms which are mostly parasitic with few free living. The study of Platyhelminthes is called Helminthology.
General Characteristic of Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Body is dorso-ventrally flattened and leaf like.
- They are mostly parasitic with few free living.
- They are bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic. Body is covered with ciliated epithelium or thin cuticle.
- Outer layer is ectoderm, middle layer is mesoderm and inner layer is endoderm. Mesoderm consists of parenchymal cells which acts as transport and supporting medium.
- Mode of nutrition is holozoic type. Parasitic worms feed on blood, bile and juice of host.
- Digestive system is incomplete or absent. Digestive system is completely absent in tapeworms where food is absorbed through general body surface.
- Respiration is aerobic in free living forms and anaerobic in parasitic forms. Gases exchange takes place through general body surface.
- Circulatory system is absent.
- Excretion takes place by specialized organ called protonephridia or flame cell or solenocytes. Anus is absent instead a pore is present at posterior end. Excretory waste is composed of ammonia, fatty acids and CO2.
- Nervous system is primitive and ladder like. It consists of brain, ganglion and nerve fibers.
- Reproductive system is well developed and complex. Organism are hermaphrodite or bisexual. Most advanced type of reproduction is found in parasitic forms. They also posses high power of reproduction.
- Fertilization is internal with cross fertilization. Parthenogenesis is commonly seen in parasitic forms.
- Development is through direct process in free living but indirect development is dominant in parasitic forms. Larva in indirect development is free swimming.
- Life cycle of free living flatworm is simple. But parasitic forms have complex life cycle including one or two host. Germinal lineage hypothesis is the most accepted theory for explaining life cycle of parasitic worms.
Classification of Phylum Platyhelminthes
Phylum Platyhelminthes is classified into 3-classes on the basis of mode of life, presence or absence of digestive system and cilia on the body.
- Turbellaria
- Trematoda
- Cestoda
Turbellaria
(L; turbella = a string)
- Mostly free living aquatic forms.
- Body unsegmented.
- Hooks and sucker totally absent.
- Epidermis is cellular covered with cilia.
- Digestive system consists of mouth, pharynx and intestine.
- Development is direct. Regeneration is common.
- Examples: Planaria, Bipalium, Mesostoma etc.
Trematoda
(Gr; trema = hole; eidos = form)
- Exclusively parasitic including both ectoparasite and endoparasite.
- Body unsegmented.
- Hooks absent and sucker present.
- Cilia and epidermis both absent.
- Digestive system consists of mouth, pharynx and intestine.
- Development is direct in ectoparasite. Indirect development in ectoparasite including different larval forms.
- Examples: Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke), Schistosoma (blood fluke), Polystoma (bladder fluke), Fasciola buski etc.
Cestoda
(Gr; kestos = gridle; eidos = form)
- Exclusively endoparasite.
- Body segmented.
- Hooks and sucker both present.
- Cilia and epidermis both absent.
- Digestive system is completely absent.
- Development is Indirect through different larval forms.
- Examples: Taenia solium (park tapeworm), Taenia saginata (beef tapeworm), Echinococcus granulosus (dog tapeworm), Hymeolepisnana etc.
Examples of Platyhelminthes
Examples of Platyhelminthes with their common name.
| S.N | Examples of Platyhelminthes (Scientific Name) | Common Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dugesia | Planaria |
| 2 | Bipalium | Hammer head worms/broadhead planarians |
| 3 | Convoluta | Acoelomorph flatworm |
| 4 | Fasciola hepatica | Liver fluke |
| 5 | Paragorimus westermani | Lung fluke |
| 6 | Polystoma | Bladder fluke |
| 7 | Schistosoma | Blood or lymphatic fluke |
| 8 | Taenia saginata | Beef tapeworm |
| 9 | Echinococcus granulosus | Dog tapeworm |
| 10 | Taenia solium | Pork tapeworm |
| 11 | Diphyllobothrium latum | Fish tapeworm |
| 12 | Hymenolepisnana | Dwarf tapeworm |
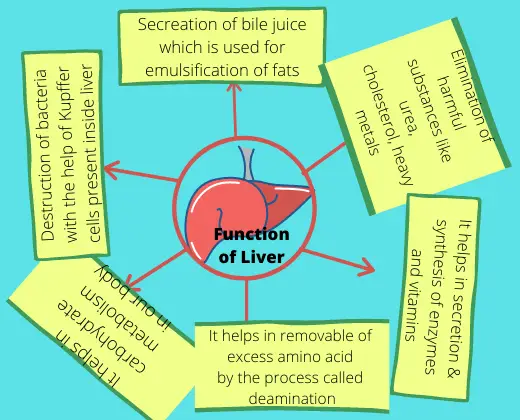
Importance of Platyhelminthes
Platyhelminthes are mostly harmful due to their parasitic and diseases causing agent. There are some useful importance also.
Economic Importance
Platyhelminthes plays role in maintaining ecosystem. It helps in maintaining food chain.
Medicinal Uses
- Helminth therapy is a type of immunotherapy to treat autoimmune diseases and immune disorders by infecting patient with intestinal parasites.
- Endoparasite like tapeworms are used for weight loss. Light infections of adult tapeworm can loss 1-2 pound per week. It is sold as weight loss pills in US & Mexico. Treatment cost approx. $1500.
Harmful Aspects
- Most of the Platyhelminthes cause disease in animals.
- Liver rot is caused by Fasciola hepatica.
- Taeniasis is caused by Taenia solium.
- Schistosomiasis is caused by Schistosoma.
Conclusion / Important Points
- Platyhelminthes are the first animals to have organs.
- Platyhelminthes lacks skeletal system, circulatory system, respiratory system. immune, lymphatic or endocrine systems
- Excretion takes place by flame cells or solenocytes or protonephridia.
- Between alimentary canal and body wall, parenchyma is present.
- They are mostly hermaphrodite except blood fluke.
References
1. https://biosurvey.ou.edu/Invert_manual/Platyhelminthes1.html
2. Jordan EL and Verma PS. 2018. Invertebrate Zoology. 14th Edition. S Chand Publishing.
3. https://www.austincc.edu/sziser/Biol%201413/LectureNotes/lnexamII/Phylum%20Platyhelminthes.pdf