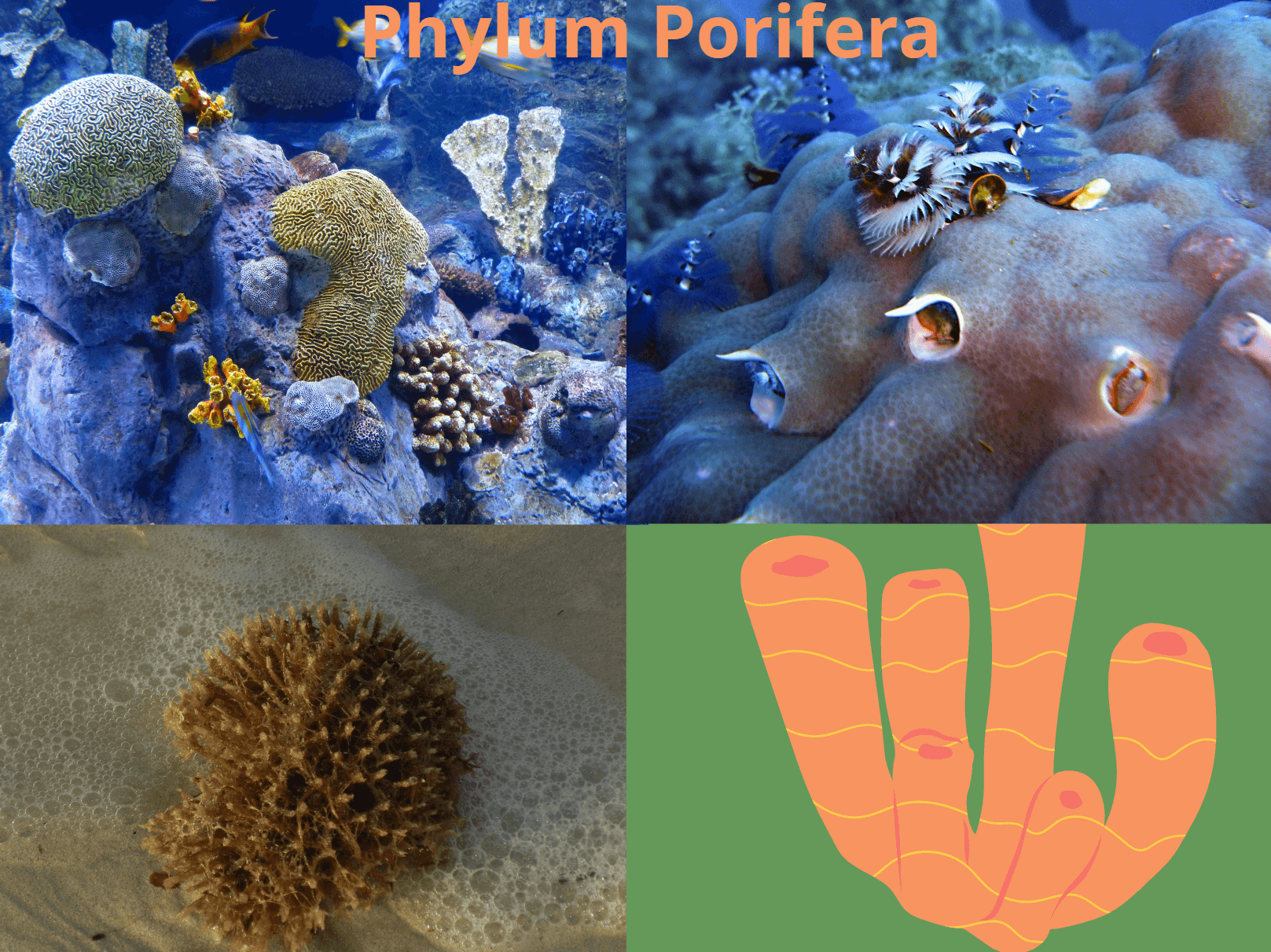
Porifera is only phylum belonging to subkingdom Parazoa. The word porifera is derived from Latin word porus = pore and ferre = to bear. They are soft, primitive, multicellular with pores on their body surface. Porifera are commonly called as sponges. The study of porifera is called Parazoology. Robert E. Grant coined the term porifera. John Ellis study water canal system in 1765 which proof the animal nature of sponges. It consists of about 5,000 living species having majority belonging to marine species and about.

Characteristic Features of Porifera
Habitat: They all are aquatic, mostly marine with some fresh water habitat. It is cosmopolitan in distribution ranging from polar tropics region. Out of total species of porifera, about 150 species are fresh water habitat. They are attached to substratum (i.e. sessile). They may be solitary as in sycon or colonial as in Leucosolenia. The larval forms are free living.
Body Organization: They are multicellular with cellular grade of organization. Tissues are absent. The cells show physiological division of labor which performs certain activities.
Read Also: Phylum Coelenterata in detail
Germ Layers: They are diploblastic. Outer layer is called pinacoderm while inner layer is called choanoderm. Pinacoderm consists of pinacocytes cells. Choanoderm consists of choanocytes cells. Between two germs layer, a gelatinous material called mesenchyme is present.
Choanocytes which are also called as collar cells are characteristic features of all sponges. Collar cells are only found in sponges (porifera).
Symmetry: They are mostly asymmetry with some possessing superficial radial symmetry.
Coelom: They are acoelomate animals.
Locomotion: They do not show location. That’s why called as sessile organism which remains attached to substratum.
Nutrition: It is holozoic type.
Digestion: They do not posses mouth, instead they have small openings throughout their body called as ostia. Water enters through ostia into choanoderm where it gets filtered by flagellated cells called choanocytes. During filtration process, small food particles are filtered from water current and digest it inside. That’s why they are also called as filter feeder. Digestion is intracellular.
Respiration: Respiratory organs are absent. It takes place by simple diffusion.
Skeleton of Sponges: Skeletons are present in sponges. Skeleton provides support to the soft body. Skeleton of sponges consists of spicules or spongin fibers. Spicules are calcareous or silicious in nature.
The cells secreting spicules are called scleroblasts. Scleroblast are of three types calcoblasts, silicoblast and spongioblast.
Canal System: Presence of canal system is characteristic features of sponges. It is also called aquiferous system. It helps in continuous supply of water current in their body. Respiration, excretion, nutrition all takes place with the help of water current flowing inside the body.
There are 3-types of canal system in sponges.
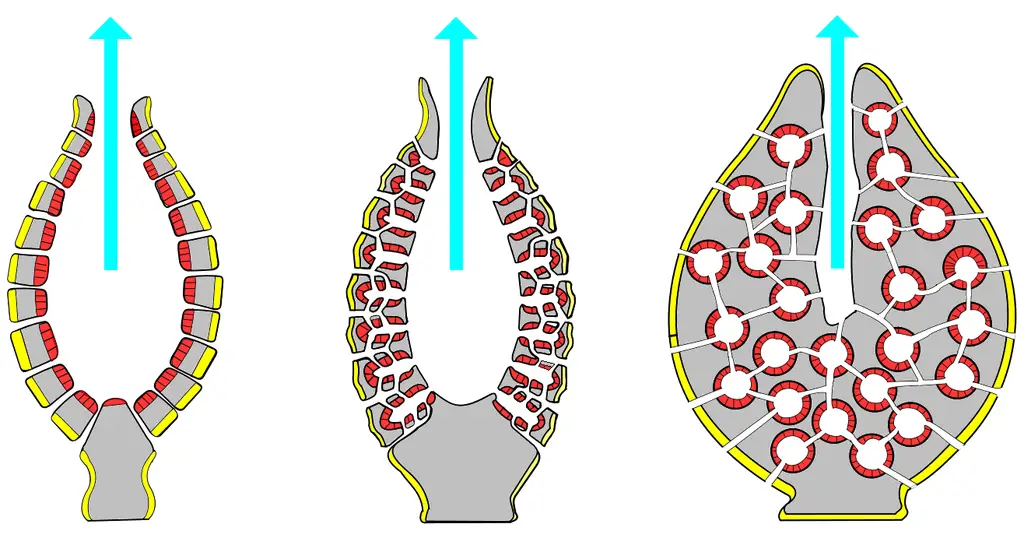
i) Ascon type: Simplest type of canal system found in asconoid sponges like Leucosolenia. Its spongocoel is lined with choanocytes.
ii) Sycon type: It is found in syconid sponges like sycon.
iii) Leucon type: It is the most complicated and primitive type of canal system found in leuconoid sponges like Spongilla, Euspongia etc.
Excretion: It also occurs by simple diffusion. Excretory wastes are mainly composed of ammonia. So, called as ammoniotelic.
Nervous System: It consists of a brain with 3 pairs of ganglia and 2 pairs of nerve cords.
Reproduction: It occurs both by asexual and sexual methods.
i) Asexual reproduction takes place by fragmentation, budding and gemmule formation. Gemmules are internal buds containing archeocytes which are mostly produced by fresh water sponges and concerned with asexual reproduction.
ii) Sexual reproduction takes place by formation of male and female gametes. They are hermaphrodite. Cross fertilization is very common.
Development: Development is indirect through formation of ciliated larva. Larva are active and free swimming. The larva of sponges are called parenchymula in Leucosolenia and amphiblastula in sycon.
Classification of Porifera
The living species of porifera is classified into 3-classes based on the nature and structure of spicules.
- Calcarea/Calcaspongiae
- Hexatinellida/Hyalospongiaes
- Demospongia
Calcarea
(L. calx=lime)
- All species are marine.
- Body is cylindrical in shape.
- Presence of calcareous spicules made of calcium carbonate (CaCO3).
- Canal system is ascon or sycon type.
- Examples: Sycon, Leucosolenia, Grantia etc.
Class calcaea is furher divided into 2 orders.
Order 1. Homocoela (=Asconosa)
Order 2. Heterocoela (=Syconosa)
Hexactinellida
(Gr., hex=six + actin=ray)
- All species are marine.
- Body is cup, funnel or cylindrical shape.
- Presence of silicious spicules made of silica.
- Canal system is ascon or sycon type.
- Examples: Euplectella (Venus flower basket), Hyalonema (Grassrope sponges), Pheronema etc.
Class Hexactinellida is further divided into 2 orders.
Order 1. Hexasterophora
Order 2. Amphidiscophora
Demospongia
- Species are marine as well as fresh water.
- It includes largest sponges.
- Body is compact, massive and variable in shape.
- Presence of silicious spicules.
- Canal system is leucon type.
- Examples: Spongilla, Euspongia, Chalina etc.
Class Demospongia is further divided into 3 sub classes and their respective orders.
Subclass I: Tetractinellida
Order 1. Myxospongida
Order 2. Carnosa
Order 3. Choristida
Subclass II: Monaxonida
Order 1. Hadromerina
Order 2. Halichondrina
Order 3. Poecilosclerina
Order 4. Haplosclerida
Subclass II: Keratosa
Examples of Porifera
Some examples of Phylum porifera with their common names is tabulated below.
| Examples of Porifera (Scientific Name) | Common name |
|---|---|
| Sycon | Crown sponge |
| Leucosolenia | Calcareous sponges |
| Euplectella | Venus flower |
| Hyalonema | Glass rope sponge |
| Pheronema | Bowl sponges |
| Spongilla | Fresh water sponge |
| Hippspongia | Horse sponge |
| Eupongia | Bath sponge |
| Chlina | Mermaid’s glove |
| Cliona | Boring sponge or sulphur sponge |
Importance of Porifera
Sponges are used for various purposes. They are economically as well as medicinally important.
Economic Importance
- It has a wide variety of species which forms a vast ecosystem in oceans.
- Sponges like are used as food
- It is used in manufacturing of ceramics and clay utensils.
- It contains pigments which are used to coloring purposes.
Medicinal Importance
- Some species of sponges produces toxins which inhibits growth of certain organism. This character is used being researched for inhibiting growth of certain bacteria and in nerve impulse conduction.
- Certain sponges are also found to contain antibacterial, antiviral, antifungal, antimalarial, immunosuppressive properties which can be used for medicinal purposes.
Referances
1. https://manoa.hawaii.edu/exploringourfluidearth/biological/invertebrates/phylum-porifera
2. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sponge
3. Jordan EL and Verma PS. 2018. Invertebrate Zoology. 14th Edition. S Chand Publishing.



