Mollusca is one of the phylum of kingdom animalia which is characterized by soft body. Lamarck coined the term ‘Mollusca’. It is the second largest phylum after Arthropoda. Malacology is the study of Mollusca whereas conchology is the study of cells of Mollusca. It consists of approximately 90,000 species.
Characteristic Features of Mollusca
Habitat: They are mostly marine with some freshwater and few terrestrial forms. They are cosmopolitan in distribution. Most of them feeds on small plants and phytoplankton found in sea, oceans, lakes and damp soil. So, it is mainly herbaceous in nature but some species are active predators such as squids.
Germ layers: They are triploblastic.
Symmetry: Usually bilaterally symmetry except gastropods which are asymmetric due to twisting or torsion which occurs during developmental stage. Torsion is the rotation of posterior part of body at an angle of 180°.
Coelom: They are haemocoelomate animals due to the presence of blood spaces in the tissue.
Body Division: Body is divided into 4-parts namely: head, mantle, visceral hump and foot. In some species body may be externally or internally covered by shell whereas it may be totally absent in other species. Shell is hard in nature which serves as protective organ. Shell present in Mollusca is made up of calcium carbonate which is secreted by columnar epithelial cells of mantle.
Locomotion: Ventral muscular part acts as foot for moving and creeping. It may also be modified for borrowing.
Digestive System: Digestive system is simple and complete. It also contains digestive gland called hepatopancreas. Buccal cavity (mouth) has radula which bears minute chitinous teeth for feeding except in class Bivalvia. Posterior opening (i.e. anus) is located at mantle cavity.
Radula with chitinous teeth. Image source: wikipedia
Respiration: It takes place by feather like gills or ctenidia in aquatic forms and through lungs in terrestrial species.
Circulatory System: It is of open type except Cephalopods where it is closed type. Heart is dorsally present with 1 or 2 atrium and 1 ventricle. Blood is blue in colored due to the presence copper containing compound, haemocyanin. Haemocyanin is the respiratory pigment in Mollusca.
Excretion: It takes place by paired metanephridia or kidney. It is also called as Kaber’s organs or organ of Bojanus.
Nervous System: It consists of a brain with 3 pairs of ganglia and 2 pairs of nerve cords.
Sense Organs: Sense organs includes one pair of eyes, one pair of tentacles, statocysts (maintain equilibrium of body) and osphradium (chemoreceptor for testing nature of water).
Reproductive System: Sexes are usually separate but some are hermaphrodite (organism having both male and female reproductive system). Gonads with ducts are present.
Fertilization may be external or internal. Mostly oviparous.
Development: Development is indirect. Larva of Mollusca is called as trochophore or veliger or Glochidium (parasitic form). But direct development is found in class Cephalopoda.
Classification of Mollusca
Phylum Mollusca is classified into different classes on the basis of shell and muscular foot.
1. Aplacophora
- Epidermis secretes aragonite spicules which covers the body.
- They are also called as solenogasters
- Both shells and foot are absent.
- Examples are: Neomenia, Chaetoderma etc.
2. Monoplacophora
(Gr. Mono; one + plax; plate + pherein; bearing)
- They are the most primitive Mollusca resembling the characteristics of Annelida.
- Only Mollusca having segmentation.
- Shell present in it is cap or dome shaped with flat foot.
- Head is distinct without eyes and tentacles.
- Examples: Neopilina
3. Gastropoda
(Gr. Gater; belly + podos; foot)
- Largest class of phylum Mollusca.
- Hard spiral shaped shell is present which covers the body.
- Asymmetrical body organization.
- Foot is large and flat, used for locomotion.
- Visceral torsion occurs during developmental process in which the posterior part of body is rotated by an angle of 180°.
- Head with distinct eyes and tentacles.
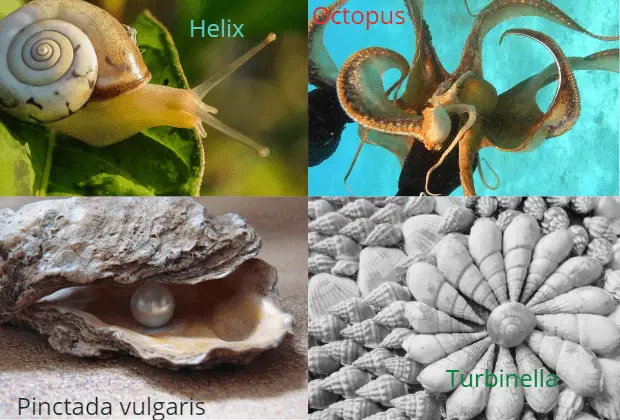
- Examples: Pila (Apple snail), Helix (Garden snail), Limax (slug), Turbinella (shankha) etc.
4. Scaphopoda
(Gr. Scapha; boat + podos; foot)
- Body covered by hard shells.
- Foot is pointed and reduced modified for burrowing/digging.
- Exclusive marine.
- Bilaterally symmetrical.
- Heat with eyes and tentacles.
- Commonly called as tooth shells or tusk shells.
- Examples: Dentalium (Elephant’s tusk shell), Cadulus.
5. Pelecypoda/Bivalvia
(Gr. pelekus; hatchet + podos; foot)
- Foot is laterally compressed and used for burrowing.
- Body is covered inside two valves of shell.
- No distinct head without eyes and tentacles.
- Cilia present in gills help in feed. Generally, they are filter feeder.
- Examples: Unio (fresh water mussels), Mytilus (Sea water mussels), Teredo (Ship worm), Pinctada vulgaris (Pearl oyster).
6. Cephalopoda/Siphonopoda
(Gr. kephale; head + podos; foot)
- Most specialized Mollusca.
- Foot is modified into arms and suckers.
- Bilaterally symmetrical body.
- Marine, free swimming and carnivorous.
- Development is direct.
- Ink gland usually present for defense.
- Locomotion takes place by special water expelling system called as jet propulsion or siphon jet system.
- Shells may or may not be present.
- Examples: Octopus, Sepia etc.
7. Amphineura
(Gr. Amphi; both + neuron; nerve)
- They are commonly called as chitons.
- Shells consists of mid dorsal row with 8 longitudinal plates.
- Bilaterally symmetrical and dorsiventral flattened body.
- Head distinct without eyes and sensory tentacles.
- Foot is flat used for creeping.
- Examples: Chiton, Tonicella etc.
Examples of Mollusca
Examples of Mollusca with their common and their scientific name.
| S.N | Scientific Name | Common Name |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pila | Apple Snail |
| 2. | Helix | Garden Snail |
| 3. | Limax | Slug |
| 4. | Doris | Sea Lemon |
| 5. | Aplysia | Sea Hare |
| 6. | Dentallium | Elephant’s tusk shell |
| 7. | Unio | Fresh water mussel |
| 8. | Solen | Razor clam |
| 9. | Teredo | Ship worm |
| 10. | Pinctada vulgaris | Pearl oyster |
| 11. | Octopus | Devil fish |
| 12. | Loligo | Squid |
| 13. | Architeuthis | Giant squid |
| 14. | Turbinella pyrum | Chank shell or Chank |
Importance of Mollusca
Mollusca are economically and medicinally beneficial to human. From ancient time, different species of Mollusca is used in treatment of diseses, fooder, making jewelry etc. Some species are also found to be harmful.
Economic Importance
Many Molluscans like Sepia, Octopus, Mussels are fished world widely which are used for food. It is also the major economic source for most people living near seas and oceans. They also form the part of fisheries and agriculture industries.
Pear oyster produces valuable pearl which is used as jewelry. Genus Pinctada produces the most valuable and precious pearls.
The shell produced form Turbinella pyrum is called as ‘chank’ which is used as trumpet in Hindu temples and in manufacturing bangles.
Snail are the intermediate host of Fasciola hepatica and Schistosoma which is an important vector for completing their life cycle during development.
Good quantities of shells are used in cement and chalk industries.
Small gastropods like squid are used as bit for fishing.
Medicinal Importance
Some oyster shells like Olympia oyster are used as supplement of calcium in both animals and human.
Threads produced by mussels during attachment are called as byssal threads which are thought to be possible blue for surgery.
In many traditional cultures, powder of oyster shells are taken to treat acid indigestion, fatigue and stopping hemorrhage.
Slugs and snails are used in many countries like USA, UK, Italy, Greek for treatment of stomach ulcers, bronchitis and asthma. It is swallowed live or by making soup in many countries.
The venom of some cone shells is found to be effective treatment of strokes and heart diseases.
Harmful Aspects
Some terrestrial Mollusca like Snail & Slug feeds on garden plants causing damages to plants. It also feed on mushroom causing destruction of foliage parts.
Teredo which is called as ship worm bores holes in wooden parts of ship causing millions of destructions each year.
Some gastropods cause millions of damages to oyster industries as they drill the oyster shell which reduces the production of pearls.
Interesting Facts on Phylum Mollusca
Japan is the oldest and largest pear producing country in the world. Recently China is taking the first place.
Neoplina is the connecting link between Annelida and Mollusca.
Octopus has 8 arms and is commonly called as devil fish. It does not have shell.
Green gland is the digestive gland found in unio and is comparable to liver of vertebrates.
Ink gland is especially present in squids of Cephalopods which plays role in defense mechanism.
Pinctada vulgaris is known as pearl oyster.
Pearl is secreted by columnar epithelial cells of mantle.
Pearl is formed in response to external particles when attached to skin which cause irritational sensation in them.
The first formed shell of unio is called umbo and is the thickest of all.
Body of Mollusca is unsegmented except Neoplina.
Shells of Mollusca is calcareous i.e. made up of calcium carbonate.
Rasping organ called radula is distinguishing feature of Mollusca.
Fish which are Mollusca are Sepia (Cuttle fish) and Octopus (Devil fish).
References
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mollusca
2. https://ucmp.berkeley.edu/taxa/inverts/mollusca/mollusca.php
3. Jordan EL and Verma PS. 2018. Invertebrate Zoology. 14th Edition. S Chand Publishing
4. https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/abs/10.1098/rstb.1996.0143